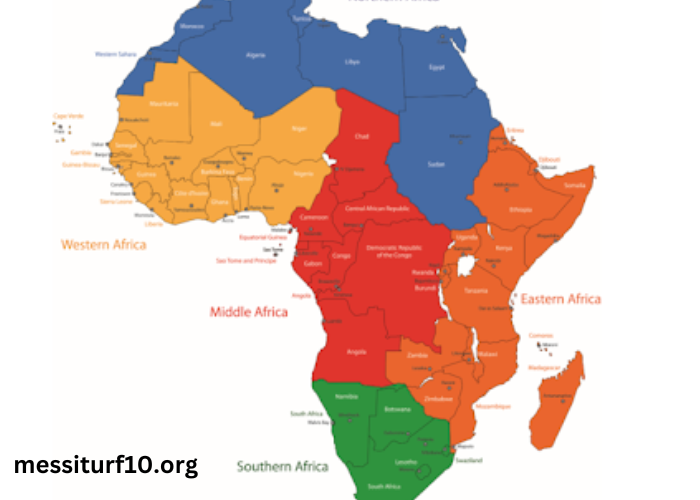
Africa, the second-largest continent, is often referred to as the cradle of humanity. Its immense size, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural heritage make it one of the most fascinating regions on Earth. Carte DE L’Afrique serves as a visual representation of this complexity, allowing individuals to appreciate the continent’s geographical and cultural diversity. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of Africa’s geography, the historical significance of its regions, the cultural richness that defines its people, and how these elements converge to create a unique identity for the continent.
Understanding Africa’s Geography
Africa’s geography is incredibly diverse, encompassing vast deserts, lush rainforests, expansive savannas, and towering mountain ranges. This diversity is not just aesthetic; it plays a crucial role in shaping the lives of the continent’s inhabitants.
To the north, the Sahara Desert stretches across several countries, serving as one of the largest hot deserts in the world. This arid landscape is characterized by its vast sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and scarce water sources. Yet, it is also home to various nomadic tribes who have adapted their lifestyles to thrive in such harsh conditions.
Moving southward, one finds the Sahel, a transitional zone between the Sahara and the more fertile regions to the south. The Sahel is marked by its semi-arid climate and serves as a crucial area for agriculture and livestock grazing. It is here that many communities engage in subsistence farming, relying on seasonal rains to sustain their crops.
Further south, the African Great Lakes region is renowned for its stunning bodies of freshwater, including Lake Victoria, Lake Tanganyika, and Lake Malawi. These lakes not only provide essential resources for millions of people but also support diverse ecosystems teeming with wildlife.
In East Africa, the Great Rift Valley emerges, a geological wonder characterized by its dramatic landscapes, including volcanic mountains and expansive valleys. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak, stands majestically in this region, attracting adventurers and tourists from around the globe.
The southern region of Africa features the Kalahari Desert and the Namib Desert, alongside rich savanna ecosystems that host an array of wildlife. This area is home to iconic national parks like Kruger National Park in South Africa and Etosha National Park in Namibia, which are vital for wildlife conservation and tourism.
The Historical Significance of Africa’s Regions
Africa’s history is as varied as its geography, shaped by millennia of human habitation, migration, and cultural exchange. Each region boasts a unique historical narrative that has influenced its present.
North Africa has long been a crossroads of civilizations, influenced by various cultures from the Mediterranean and the Middle East. The ancient Egyptians, renowned for their monumental architecture and advancements in various fields, laid the foundations for much of what is known about ancient civilization. The legacy of the Pharaohs, along with the rich history of Carthage and the influence of the Roman Empire, continues to shape the region today.
Sub-Saharan Africa presents a different historical landscape, marked by the rise and fall of powerful kingdoms and empires. The Ghana Empire, Mali Empire, and Songhai Empire dominated West Africa for centuries, facilitating trade across the Sahara and fostering a rich cultural exchange. The legendary city of Timbuktu became a center of learning and culture, attracting scholars from various regions.
The East African coast witnessed the emergence of the Swahili city-states, which thrived on trade between Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. This trade network facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures, leading to the rich Swahili culture that still exists today.
In Southern Africa, the arrival of European colonizers during the Age of Exploration led to profound changes. The impact of colonialism is still felt today, with various nations grappling with their colonial pasts and striving for economic and political independence.
The Cultural Tapestry of Africa
Africa’s cultural diversity is one of its most captivating features, with over 3,000 ethnic groups and more than 2,000 languages spoken across the continent. Each group contributes to the rich tapestry of African culture, reflecting its history, beliefs, and traditions.
Music and dance play a vital role in African culture, serving as expressions of identity, community, and spirituality. Traditional African music varies widely from region to region, incorporating diverse instruments, rhythms, and styles. The drum, for instance, is central to many African musical traditions, often used in ceremonies, celebrations, and storytelling.
Art is another significant aspect of African culture, with each region showcasing its unique artistic expressions. Traditional crafts, such as beadwork, pottery, and textile production, often carry cultural significance, representing stories, rituals, and social status. Contemporary African artists are also gaining international recognition, using their work to address social issues and celebrate their heritage.
Religion in Africa is as diverse as its cultures, with a rich tapestry of beliefs ranging from traditional African religions to Christianity and Islam. Many communities blend elements of these religions, creating unique spiritual practices that reflect their histories and experiences.
Festivals and celebrations are integral to African culture, providing opportunities for communities to come together in joy and remembrance. Events like the Fes Festival of World Sacred Music in Morocco and the Harare International Festival of the Arts in Zimbabwe showcase the continent’s vibrant artistic expressions and cultural diversity.
The Impact of Modern Challenges
Despite its rich cultural heritage and natural beauty, Africa faces numerous modern challenges that affect its development and the well-being of its populations. Issues such as poverty, political instability, and environmental degradation pose significant obstacles to progress.
Many African nations continue to grapple with the legacies of colonialism, which have contributed to economic disparities and social inequalities. In some regions, ongoing conflicts and political instability hinder efforts to achieve sustainable development, leading to humanitarian crises and displacement.
Climate change presents another pressing challenge. Africa is particularly vulnerable to its effects, with many regions experiencing increased droughts, flooding, and changing weather patterns. These changes impact agriculture, food security, and access to clean water, further exacerbating existing challenges.
Efforts to address these issues are underway, with numerous organizations and governments working collaboratively to promote sustainable development and empower local communities. Initiatives focused on education, healthcare, and economic growth aim to create a more equitable future for the continent.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
In recent years, technology has emerged as a powerful tool for addressing some of Africa’s challenges. The continent is witnessing a surge in innovation, particularly in areas such as mobile technology, agriculture, and renewable energy.
Mobile technology has transformed communication and access to information in Africa. With a significant percentage of the population using mobile phones, businesses are leveraging this technology to enhance service delivery and reach underserved communities. Mobile banking, for instance, has revolutionized financial inclusion, enabling millions to access banking services for the first time.
In agriculture, innovations such as precision farming and mobile applications are helping farmers increase productivity and adapt to climate change. These advancements allow farmers to access real-time data on weather patterns, market prices, and best practices, leading to improved yields and income.
Renewable energy initiatives are gaining momentum across the continent, with solar power emerging as a viable solution for addressing energy shortages. Many rural communities are turning to solar energy solutions, providing clean and sustainable power while reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
The Future of Africa: Opportunities and Potential
The future of Africa is marked by both challenges and opportunities. With a young and dynamic population, the continent has the potential to drive economic growth and innovation. Investments in education, infrastructure, and technology are critical for harnessing this potential and creating a brighter future.
Emerging sectors such as technology, renewable energy, and tourism offer significant growth opportunities. By fostering an environment conducive to entrepreneurship and innovation, African nations can leverage their resources and talent to build sustainable economies.
Furthermore, the African Union and various regional organizations are working towards greater integration and collaboration among African countries. Initiatives such as the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) aim to boost intra-African trade and economic cooperation, creating a more unified and prosperous continent.
Conclusion
Carte DE L’Afrique serves as a powerful reminder of the continent’s rich geography, history, and cultural diversity. As we explore the intricacies of Africa, it becomes evident that the continent is not just a collection of nations; it is a vibrant tapestry of people, stories, and experiences.
Understanding Africa’s geography allows us to appreciate the environments that shape its communities, while the historical narratives provide context for its present challenges and opportunities. The cultural richness of Africa is a source of pride and resilience, reflecting the spirit of its people.
As we look to the future, embracing Africa’s potential and addressing its challenges will require collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to sustainable development. By celebrating the continent’s diversity and working together, we can pave the way for a prosperous and inclusive future for all Africans.